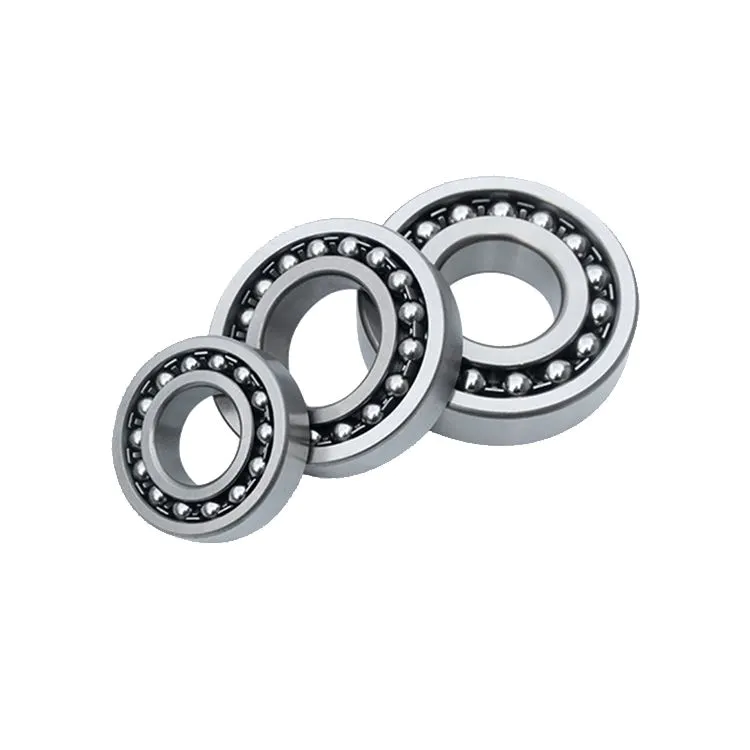
PRODUCT
The influence of alloy elements on heat treatment
by:Waxing
2020-10-03
Alloy elements on the effects of austenitizing austenitic grain in ferrite and carbide border nuclear and raised;
Residual carbides dissolve;
Austenitic composition homogenization, grew up at high temperature of austenite grain coarsening process, etc.
After adding alloying elements in steel on the three process have great influence,
1)
Containing carbide forming elements of alloy steel and the carbide in the organization, and is more stable than cementite carbide alloy cementite or special, therefore, when austenitizing heating carbide difficult to dissolve, or need higher temperature and longer time.
Generally speaking, the alloy elements to form carbide tend to be stronger, the carbide is more difficult to dissolve.
(
2)
Alloying elements in the homogenization of austenite, also need a long time, because of alloy element diffusion velocity, were far lower than the carbon diffusion velocity.
(
3)
Some alloying elements hindering strongly austenite grain coarsening process, this is mainly related to alloy carbide hard to dissolve and undissolved carbide hindered the austenitic grain boundary migration, thus, contain strong carbide forming elements (
Such as molybdenum, tungsten, vanadium, niobium and titanium, etc. )
Steel, the austenitizing when heated, easy to get fine grain group.
The alloy elements on the influence of austenite grain coarsening process, generally can be summarized as follows: 1)
Strong prevent grain coarsening elements: titanium, niobium, vanadium, aluminum, etc. , which has the strongest in titanium.
2)
Tungsten, molybdenum, chromium strong carbide forming elements, also significantly hinder the austenite grain coarsening process.
3)
Generally considered silicon and nickel can also hinder the austenite grain coarsening, but the effect is not obvious.
4)
Manganese and phosphorus is the elements of austenite grain coarsening.
Alloying elements on most of the effect of austenite decomposition transformation alloy elements at a slower pace of transformation of austenite decomposition, namely C curve move to the right, is to improve the hardenability of steel.
The influence of alloy elements on martensitic transformation increases the cooling time, reduce the cooling rate.
In addition, the alloy elements on martensitic transformation temperature (
Ms points)
Has obvious influence.
Most of the alloy elements are made of martensitic transformation temperature (
Ms points)
Reduction, in which the role of manganese, chromium, nickel is the strongest, only aluminum, cobalt is by Ms.
The influence of alloy elements on tempering transformation of alloy elements on the influence of the quenching steel tempering transformation mainly has the following three aspects.
(
1)
Tempering stability of steel in the process of the main performance of alloy elements on tempering to delay the decomposition of martensite and retained austenite transformation, improves the recrystallization temperature of ferrite and carbide hard to gather grow to keep a larger dispersion degree, thus raising the steel to temper softening resistance, which improves the tempering stability of steel.
(
2)
Produce some secondary hardening alloy element in steel, when the tempering, the hardness of steel is not as has been the rise of tempering temperature, but after reaching a certain temperature, hardness increased, and with the further increase of the tempering temperature, the hardness also increases further, until the peak.
This phenomenon is called secondary hardening tempering process.
Tempering secondary hardening phenomenon and precipitates on the properties of alloy steel tempering.
When the tempering temperature below 450 ℃, precipitation in steel cementite, above 450 ℃ cementite dissolving, began to precipitate out the dispersion stability of refractory in steel carbide Mo2C, VC, etc, make the hardness of steel began to rise, and in 550 ~ 600 ℃ or so precipitate out process is complete, the steel hardness peak.
(
3)
Increasing the temper brittleness first appeared in the process of steel in tempering b temper brittleness,
250 ~ 400 c tempering)
T the tempered martensite brittle and the second category of temper brittleness,
450-600 - C tempering)
, that is, high temperature tempering brittleness are related to the existence of alloying elements in steel.
Custom message