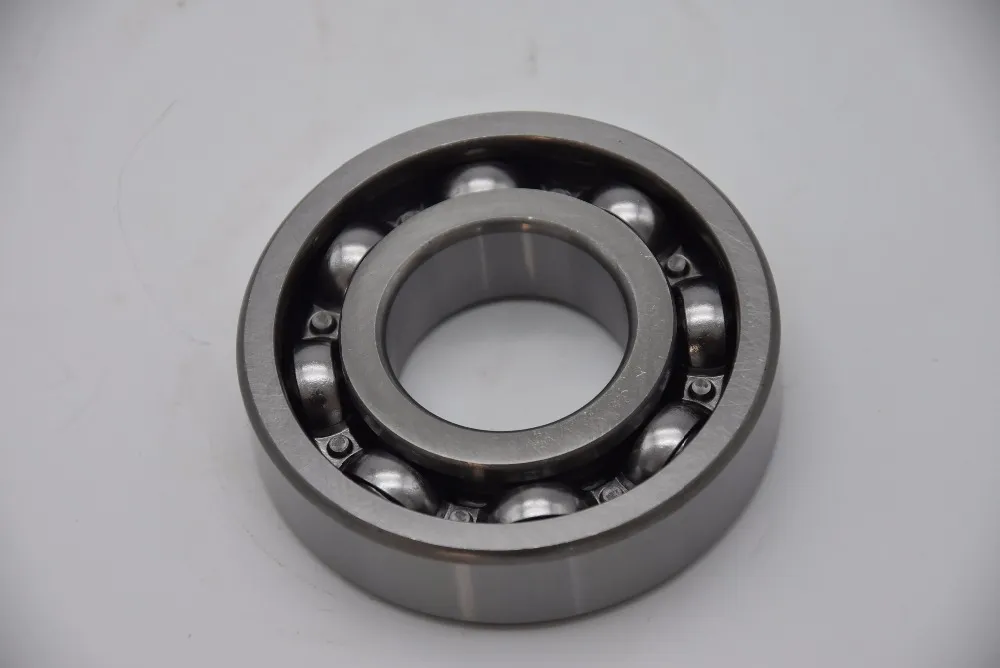
PRODUCT
The types of tempering hardenability
by:Waxing
2020-10-04
1, 270 ℃ ~ 350 ℃ embrittlement: also known as low temperature tempering hardenability, occurs mostly in carbon steel and low alloy steel.
2, 400 ℃ ~ 550 ℃ embrittlement: usually structure using alloy steel embrittlement phenomenon caused by the temperature range.
3, 475 ℃ embrittlement, particularly to Cr content is more than 13% of ferritic stainless steel iron, between 400 ℃ to 550 ℃ with tempering treatment, the hardness and embrittlement phenomenon, at about 475 ℃ is particularly significant.
4, 500 ℃ ~ 570 ℃ embrittlement: common to machining tool steel, high speed steel and other materials, the temperature will be precipitation carbides, cause secondary hardening, but also leads to the increase of brittleness.
(
3)
The influence of alloy elements on tempering transformation hardening alloy steel during tempering, the microstructure transformation is similar to carbon steel.
But because of the addition of alloy elements, in the tempering transformation has the following characteristics: 1, improve the quenching tempering stability of steel quenching steel during tempering, intensity, hardness drop resistance called tempering stability.
2, produce secondary hardening quenching steel in 500 ~ 600 ℃ temperature range tempering, increase hardness, known as the secondary hardening.
3, produce temper brittleness quenching steel at a certain temperature range tempering, impact toughness sharp decline phenomenon, called the temper brittleness.
(
4)
Cast iron tempered and quenching hardening is so-called the material since austenitic area of temperature a very fast rate cut temperature to prevent the formation of pearlite or sorbite, since the austenite zone temperature cooled to Ms will not happen because the time is too short carbon diffusion, basic directly into martensite, the organization is very hard but also very fragile, can make its soft temper, in order to improve the toughness, therefore after different temperature back to different hardness can be obtained, a combination of strength and toughness.
With the so-called constant temperature quenching or hot-melt quenching, namely in the salt bath and metal bath quenching, mesophase or change the organization of the ductile iron, quenching and tempering treatment in cast iron spheroidal graphite cast iron, for gray cast iron, no special meaning, in most to increase abrasion strength of gray cast iron quenching treatment, will consider when in fact the results achieved by surface treatment.
For spheroidal graphite cast iron, after quenching tempering treatment, can get the same intensity and casting or normalization treatment, but has a higher yield strength, the results obtained more flexible, especially high toughness, because after quenching and tempering, base with high carbon, at the same time, in this case than with bayesian organization easier for surface hardening treatment.
If in air cooling, not alloy and low alloy cast iron hardening ability is not high, so must be conducted in a certain liquid quenching, in order to avoid the quenching cracking, using the quenching liquid is best and should avoid the use of water, oil or a suspension when quenching casting internal temperature gradient, at the same time, due to time difference, along with the formation of the martensite caused by the volume change rate is not the same, the internal stress of castings increased at the same time, it is easy to form cracking or within the casting forming high internal stress, in this case, the temperature of the oil bath should be increased to 50 ~ 100 ℃, it can avoid stress form, for casting wall thickness difference is bigger, especially carefully parts of the thicker, the first to quenching liquid, so can reduce the thinner part of the thermal stress, at the same time, the oil in the oil, must be stirring, or make it flow, casting or be kept in the quenching liquid sloshing.
Cast iron of the quenching temperature should be between 820 ~ 920 ℃, and the general factory is the most commonly used temperature is between 850 ~ 900 ℃.
When the quenching temperature is too low, can cause low carbon content of austenite, soft after quenching, the strength of the martensite formed at the same time also is low, on the contrary if quenching temperature is too high, austenite in high carbon content, increased risk of cracking during quenching and formation of the retained austenite opportunity also bigger.
After quenching of cast iron is actually a high brittleness and contained within a high stress, in order to improve its hardness and toughness must after tempering treatment, its processing program similar to steel, the heating rate should be lower than 100 ℃ / hour, back to the land of HuoWen should be between 450 ~ 600 ℃, and the tempering time is about 4 hours, tempering time is too long or the temperature is too high, will be the strength and hardness decreased a lot, but can improve the flexibility, in the low temperature tempering after a long time, can cause quite a uniform of tempering effect, at the same time the whole casting the characteristics of distribution is very uniform, in order to prevent recurrence of internal stress, especially for complex castings, after tempering should be slowly cooled to below 200 ℃.
Custom message