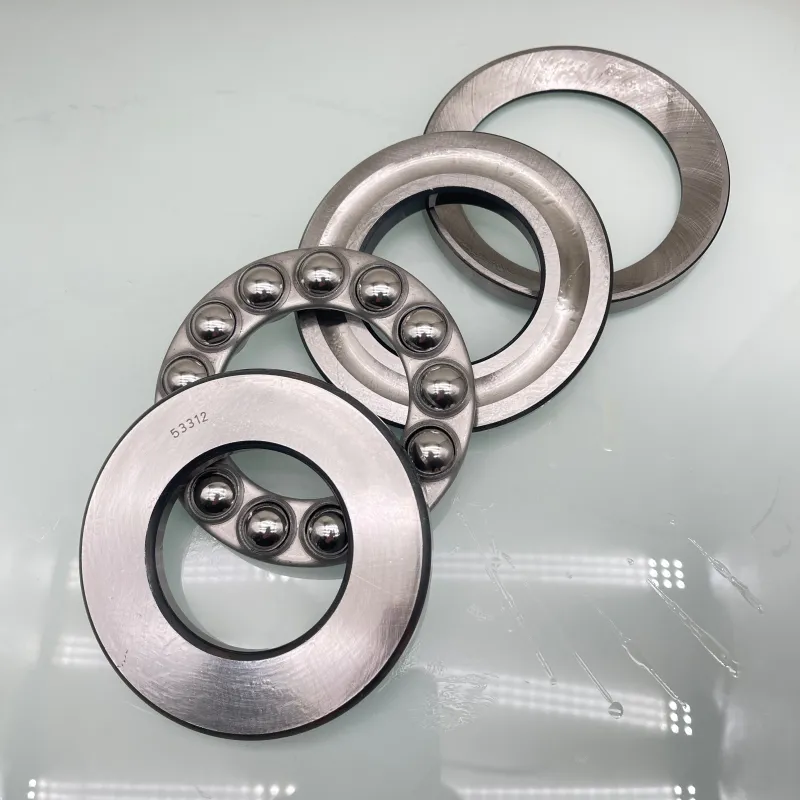
PRODUCT
The basic principle of steel ball surface heat treatment and performance are introduced
by:Waxing
2020-09-29
1.
Definition: induction heating surface quenching method is to use a certain make the workpiece surface produces a certain frequency of induced current, rapid heating of parts surface, and then rapidly quenching cooling method of a kind of heat treatment operation.
Principle: as the chart shows, electromagnetic induction to produce with the frequency of vortex induced current.
Eddy current distribution on the workpiece cross section is uneven, the heart is almost equal to zero, and the surface current density is great, known as the 'skin effect', the higher the frequency, current density greatly the thin surface layer.
Depending on the current and the resistance of the artifact itself, the workpiece surface rapidly heated to quenching temperature, while the core temperature is close to room temperature, then immediately spray water cooling, the workpiece surface hardening.
Classification: induction heating can be divided into three categories: (
1)
High frequency heating frequency is commonly used for (
200 ~ 300)
KHZ, the depth of hardening layer is (
0.
5 ~ 2.
5)
mm。
(
2)
Medium frequency heating frequency is commonly used for (
2500 ~ 8000)
HZ, the depth of hardening layer is (
2 ~ 10)
mm。
(
3)
Heating power frequency current frequency is 50 hz, don't need frequency equipment, city with alternating current (ac), hard layer depth of (
10 ~ 20)
Mm above, with alternating current (ac) the city.
Advantages and disadvantages: induction heating surface quenching heating speed, high productivity, heating temperature and the depth of hardening layer is easy to control, steel ball surface oxidation and decarburization, less deformation of steel ball is small, can make whole quenching process to realize mechanization and automation.
2 the performance of the induction surface hardening after 1.
Surface hardness, the high and intermediate frequency induction heating surface quenching workpiece, the surface hardness is often higher than ordinary quenching (2 ~ 3 units
HRC)
。
2.
Abrasion resistance, wear resistance after high frequency quenching workpiece is higher than ordinary quenching.
This is mainly because of the hardening layer martensite grain fine, carbide dispersion degree is high, and high hardness, high compressive stress on the surface of the comprehensive results.
3.
Fatigue strength: high, intermediate frequency surface quenching, thus greatly improve fatigue strength notch sensitivity.
Artifacts of the same material, the depth of hardening layer in a certain range, the fatigue strength increases with the increase of the depth of hardening layer, but the depth of hardening layer depth when the surface is compressive stress, and therefore the depth of hardening layer increased fatigue strength declines, and make the workpiece increased brittleness.
General hardening layer depth delta = (
10 ~ 20)
% D。
More appropriate, where D is the diameter of workpiece.
2.
Chemical carburizing heat treatment: carburizing is directed into the steel surface layer of carbon atoms.
Is made of low carbon steel workpiece surface layer with high carbon steel, after quenching and low temperature tempering, the workpiece surface layer with high hardness and wear resistance, and the central part of the workpiece is still maintained a low carbon steel toughness and plasticity.
Custom message